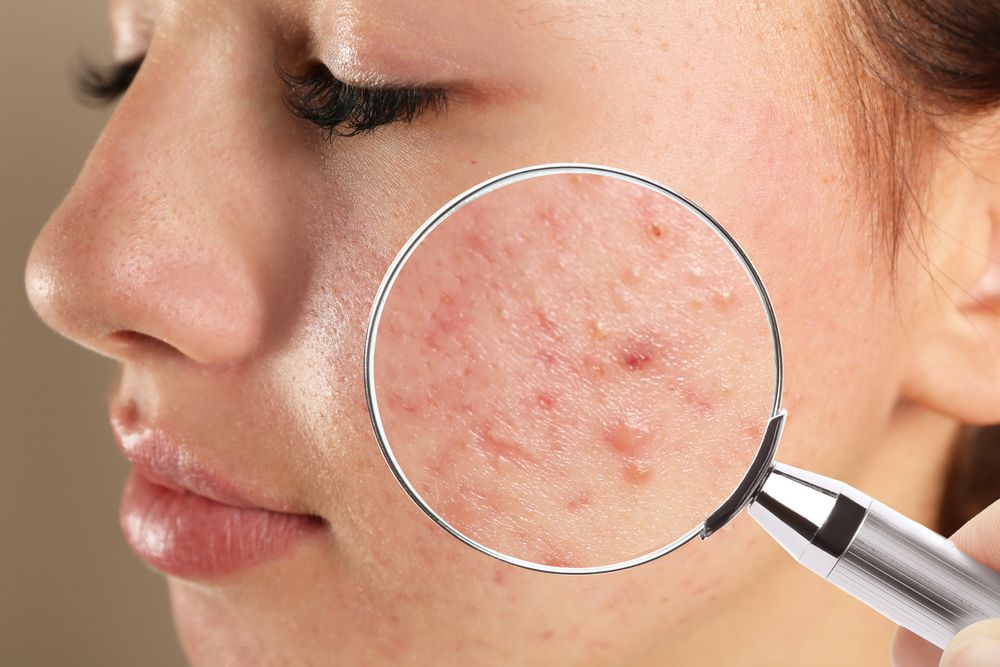
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, but it is often stigmatized and misunderstood. Acne doesn’t just impact teenagers going through puberty; it can affect people of all ages. In this blog post, we will help you decode acne by explaining its types, causes, and some of the treatment options Borealis Dermatology has available.
What Are the Different Types of Acne?
Acne is not a one-size-fits-all condition. It comes in various forms, each with unique characteristics and levels of severity. Here are the most common types of acne we help clear:
- Comedonal Acne: Comedonal acne presents itself with comedones, which can either be open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). These are non-inflammatory lesions that result from clogged hair follicles. They are usually the mildest form of acne.
- Inflammatory Acne: This category includes papules, pustules, and nodules. Papules are small, inflamed bumps on the skin’s surface that can appear red on lighter skin, while pustules contain pus. Nodules, on the other hand, are large, painful lumps that form beneath the skin. Inflammatory acne can be more uncomfortable and noticeable than comedonal acne.
- Cystic Acne: Cystic acne is among the most severe forms. It’s characterized by deep, painful cysts filled with pus that can lead to scarring. This type of acne often requires professional treatment.
What Causes Acne to Develop?
Understanding the underlying causes of acne is crucial in managing and preventing breakouts.
- Excess Sebum Production: One of the primary culprits behind acne is the overproduction of sebum, an oily substance produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands. Excess sebum can clog hair follicles, creating an ideal environment for acne-causing bacteria.
- Bacterial Infection: The bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is naturally present on the skin’s surface. However, when hair follicles become clogged, P. acnes can proliferate, leading to inflammation of the skin and formation of pimples.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, like those during puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, and even menopause can trigger acne by increasing sebum production. This is why many adolescents experience acne breakouts during puberty.
- Diet and Lifestyle Factors: Some studies suggest a link between diet and acne. A diet high in sugar and dairy products may exacerbate acne in some individuals. Stress, lack of sleep, and smoking can also contribute to breakouts.
- Genetics: If your family has a history of acne, you might be genetically predisposed to develop it as well.
What Are the Available Treatment Options for Acne?
The good news is that acne can be treated effectively through various methods:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and combat acne-causing bacteria.
- Oral Medications: For moderate to severe acne cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral antibiotics to reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth. Hormonal birth control pills are sometimes recommended for females with hormonal acne.
- Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin, often known as Accutane, is a potent oral medication reserved for severe, persistent acne. It works by decreasing sebum production and preventing clogged pores, but it comes with potential side effects and requires careful monitoring.
- Light and Laser Therapies: Light and laser treatments target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. They are particularly effective for stubborn acne cases and improving acne scars.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin’s top layer, aiding in the improvement of acne and acne scars.
- Extraction: Dermatologists can perform professional extractions to safely remove persistent blackheads and whiteheads.
- Home Care: A consistent skincare routine featuring gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and the use of non-comedogenic products can help manage and prevent acne.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle by managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and maintaining a balanced diet can complement other acne treatments.
Acne is a complex skin condition that can be physically and emotionally challenging. However, with the right understanding of its types, causes, and available treatments, you can take control of your skin’s health and regain your confidence. Remember that what works for one person may not work for another, so it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist to create a personalized acne treatment plan tailored to your needs. Don’t let acne define you; instead, take control of your skin health and regain your confidence. Contact Borealis Dermatology today at 516-246-8800, and say goodbye to acne and hello to clear, radiant skin.